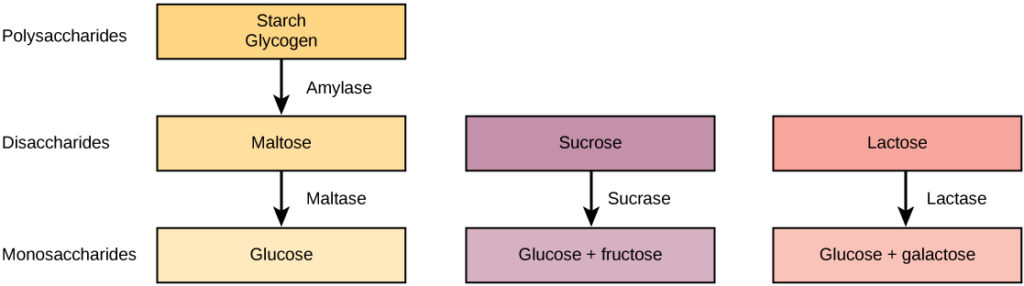
Your digestive system breaks a complex carbohydrate (starch) back down into its component glucose molecules so that the glucose can enter your bloodstream It takes a lot longer to break down a starch, however If you drink a can of soda full of sugar, glucose will enter the bloodstream at a rate of something like 30 calories per minute ACarbohydrates come from nearly all foods in your diet and eventually break down into glucose You need glucose, the simplest form ofSucrase breaks sucrose into glucose and fructose molecules Maltase breaks the bond between the two glucose units of maltose, and lactase breaks the bond between galactose and glucose Once carbohydrates are chemically broken down into single sugar units they are then transported into the inside of intestinal cells
Important Biomolecules
Carbohydrates break down into sugar
Carbohydrates break down into sugar-Although many cells use fat for energy, the brain, nerve cells, and developing red blood cells can not The body cannot convert fat into glucose to a significant degree Thus, without glucose, the body is forced to break down its protein tissues to make glucoseThe body breaks down or converts most carbohydrates into the sugar glucose Glucose is absorbed into the bloodstream, and with the help of a hormone called insulin it travels into the cells of the body where it can be used for energy People with diabetes have problems with insulin that can cause blood sugar levels to rise



Carbohydrates Ppt Download
Glucose is the body's most readily available source of energy After digestive processes break polysaccharides down into monosaccharides, including glucose, the monosaccharides are transported across the wall of the small intestine and into the circulatory system, which transports them to the liverThe body breaks down or converts most carbohydrates into the sugar glucoseGlucose is absorbed into the bloodstream, and with the help of a hormone called insulin it travels into the cells of the body where it can be used for energy Also Know, what has amylase in the saliva done to the carbohydrate in bread and rice?Carbohydrates are biological molecules made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio of roughly one carbon atom () to one water molecule ( ) This composition gives carbohydrates their name they are made up of carbon ( carbo ) plus water ( hydrate ) Carbohydrate chains come in different lengths, and biologically important carbohydrates
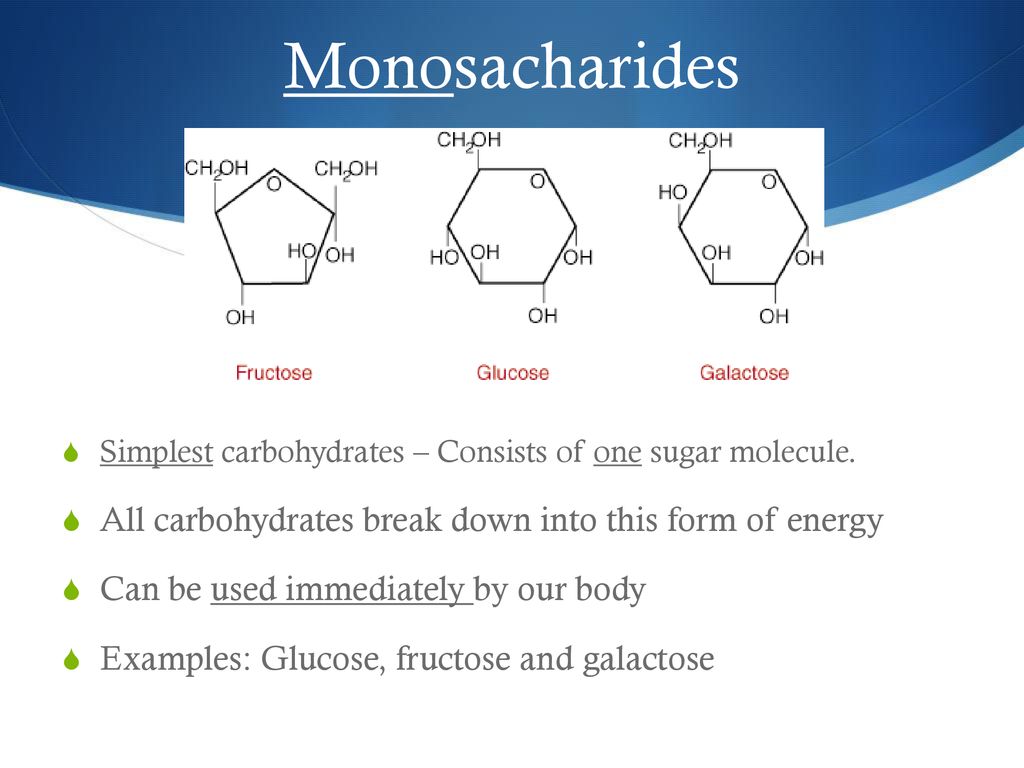
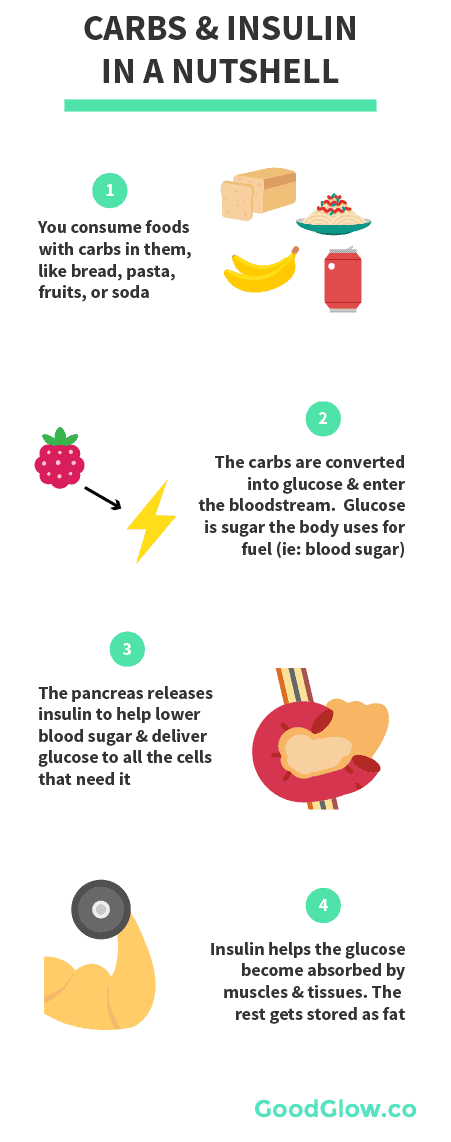
When those energy demands increase, carbohydrates are broken down into constituent monosaccharides, which are then distributed to all the living cells of an organism Glucose (C 6 H 12 O 6) is a common example of the monosaccharides used for energy productionNormally, when you eat carbs, they're broken down into small units of glucose, which end up as blood sugar When blood sugar levels go up, the pancreas responds by producing the hormone insulinCarbohydrates are well studied in terms of their implications on the gut microbiome While digestible carbohydrates, such as sugars and some starches, are turned into glucose by the small intestine for energy, others head to the colon where they are broken down
Counting carbohydrates Because carbohydrates break down into glucose, they have the greatest impact on your blood glucose level To help control your blood sugar, you may need to learn to calculate the amount of carbohydrates you are eating so that you can adjust the dose of insulin accordinglyWhen carbohydrates are digested, they break down into glucose to be either used as energy or stored in the liver and muscles for future use Advertisement Here are four the reasons why carbohydrates are important and why we need carbs in our dietsThese carbohydrates need longer to break down into glucose and provide you the most nutrients in addition to calories Refined carbohydrates are considering as bad carbohydrates, they processed to remove some parts of grains such as fibers Most common refined (processed) carbohydrates are white bread, cookies, biscuits, pastries, and all




Connections Of Carbohydrate Protein And Lipid Metabolic Pathways Boundless Biology



Carbohydrates Nutrition For Animals
Simple carbohydrates are digested very quickly and cause cause a rapid surge in blood glucose levels Your body responds promptly by releasing large amounts of insulin, to drive the glucose into most cells and restore blood glucose levels In the cells glucose is burned for energy, stored as glycogen or transformed into and stored as fatThese are hydrolyzed into glucose by different types of amylase enzyme In animals, extra carbohydrates are stored in form of glycogen Glycogen is broken down into glucose by hydrolyzing enzymes in presence of glucagon hormone Fats are triglycerides Each fat or lipid molecule is made up of one glycerol molecule, a trihydric alcoholAll carbohydrates will be broken down into simple 'glucose' or 'sugar' in our body Simple/free sugars will break down quickly, whilst complex/starchy carbohydrates will break down slowly This 'glucose' or 'sugar' is used as a source of energy by the body On a daytoday basis our bodies will use a combination of glucose, fats




23 7 Chemical Digestion And Absorption A Closer Look Anatomy Physiology



Fueling Your Body Unit 5
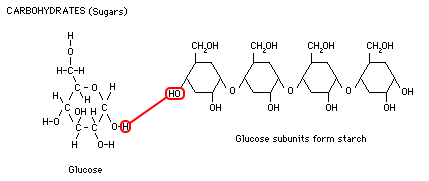
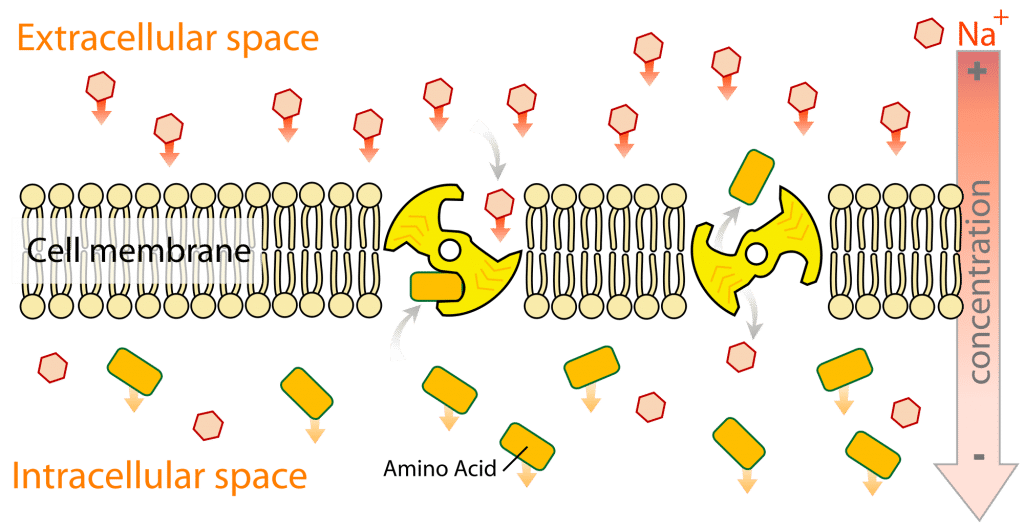
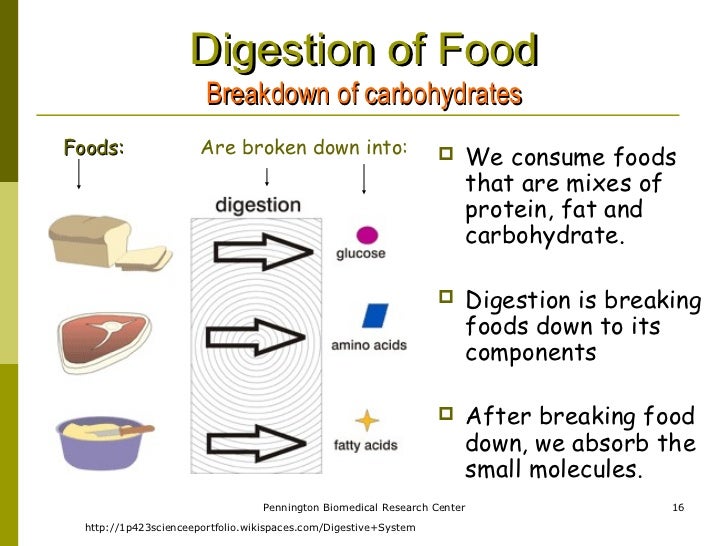
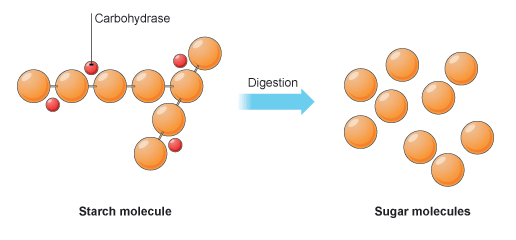
Your body needs all three forms of carbohydrates to function properly Sugars and most starches are broken down by the body into glucose (blood sugar) to be used as energy Fiber is the part of food that is not broken down by the body There are two types of fiber Insoluble fiber adds bulk to your stools so you stay regularThe starch that is consumed by humans is broken down by enzymes, such as salivary amylases, into smaller molecules, such as maltose and glucose The cells can then absorb the glucose Starch is made up of glucose monomers that are joined by α 14 or α 16 glycosidic bonds The numbers 14 and 16 refer to the carbon number of the two residuesHumans can consume a variety of carbohydrates, digestion breaks down complex carbohydrates into a few simple monomers (monosaccharides) for metabolism glucose, fructose, mannose and galactose Glucose is distributed to cells in the tissues, where it




When The Stomach Digests Food The Carbohydrates In The Food Break Down Into Glucose Stomach Small Intestines Absorb Glucose Then Release It Into Bloodstream



Small Intestine Digestion Absorption Teachmephysiology
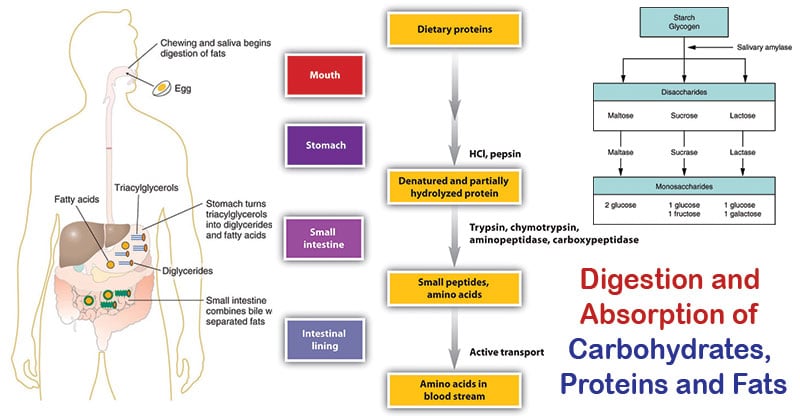
Herein, how are carbohydrates broken down into glucose?Various steps 1 Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose In some cases, this process is straightforward eg honey contains 50% sugar in the form of glucose The other 50% is in the form of fructose, which has to be converted into glucose CThey mostly break down carbohydrates and fats Once a protein source reaches your stomach, hydrochloric acid and enzymes called proteases break it down into smaller chains of amino acids How is starch broken down into glucose?



1




Carbs In A Nutshell
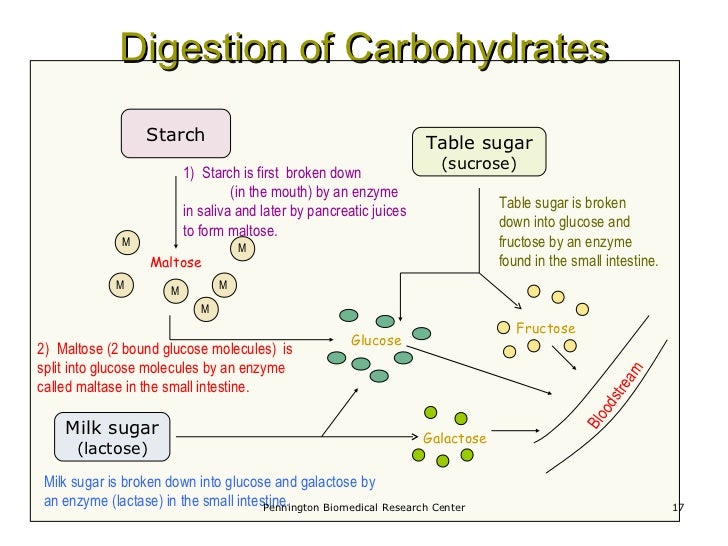
With typical refined Western diets, carbohydrate digestion is rapid and carbohydrate absorption occurs primarily in the upper small intestine Carbohydates To describe the enzymatic digestion of carbohydrates by salivary amylase 2 Starch and glycogen are broken down into glucose by amylase and maltaseSucrase breaks sucrose into glucose and fructose molecules Maltase breaks the bond between the two glucose units of maltose, and lactase breaks the bond between galactose and glucose Once carbohydrates are chemically broken down into single sugar units they are then transported into the inside of intestinal cellsWhen you eat carbohydrates in the form of sugar or starches, your body's goal, as noted by the Cleveland Clinic, is to break them down into the simple sugar, glucose, which it can use for energy The carbohydrates aren't really converted into glucose — they already contain the sugar in a more complex package




Reversing Diabetes 101 With Dr Sarah Hallberg The Truth About Carbs Blood Sugar And Reversing Type 2 Diabetes




Important Biomolecules
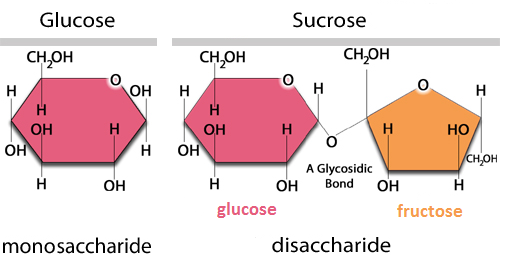
Similarly, the disaccharides sucrose, lactose, and maltose are also broken down into single units by specific enzymes (See table below) (3, 4) Absorption of Carbohydrates The end products of sugars and starches digestion are the monosaccharides glucoseStarches Plants form starches, which are also called complex carbohydrates, by stringing together sugars When you eat starchy foods, the starches are broken down into sugars, including glucose,Carbohydrates The body converts all carbohydrates into glucose, which quickly affects blood sugar levels within 12 hours after eating Carbohydrates include sugar, rice, bread, pasta, potatoes, fruits, and vegetables
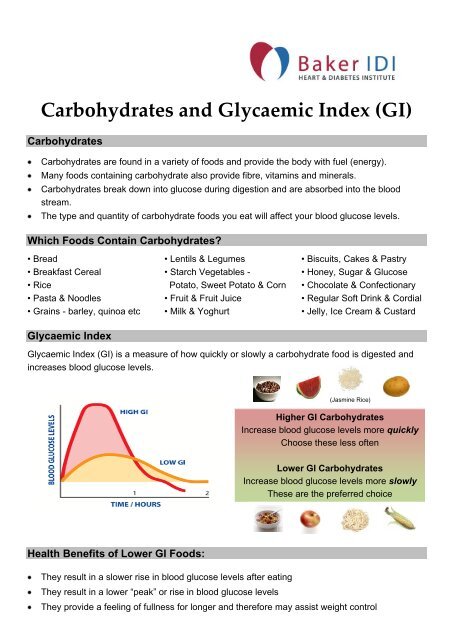



Carbohydrates And The Glycaemic Index Baker Idi
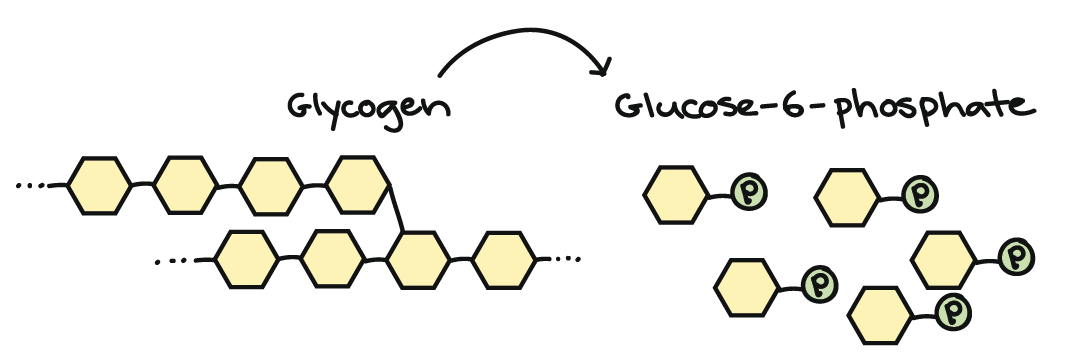



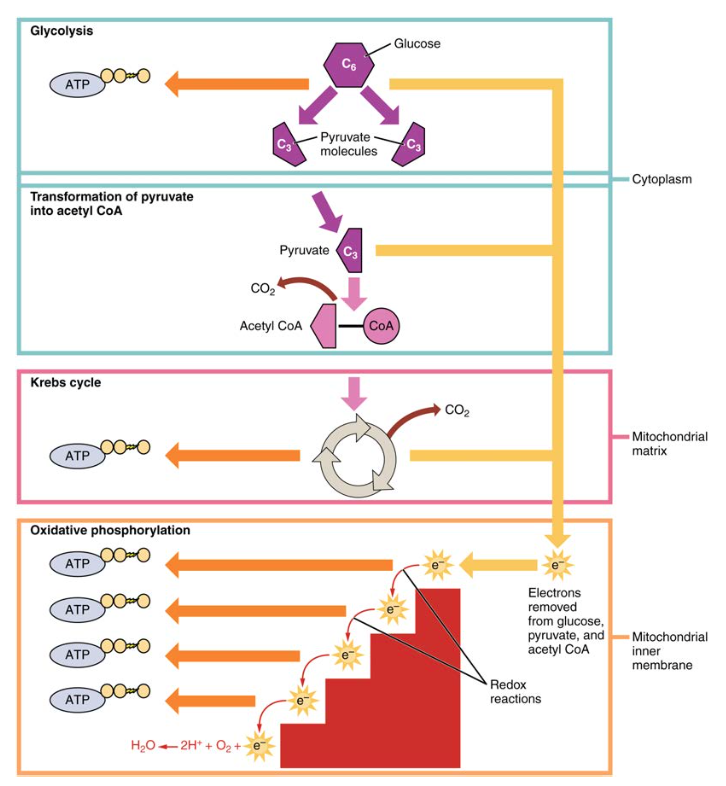
Connections Between Cellular Respiration And Other Pathways Article Khan Academy
Carbohydrates are broken down by the body into glucose, which can be absorbed into the bloodstream Once absorbed, glucose molecules travel inOnce absorbed carbohydrates pass through the liver, glucose is the main form of carbohydrate circulating in the bloodstream 4 – Large Intestine or Colon Any carbohydrates that weren't digested in the small intestine—mainly fiber—pass into the large intestine, but there's no enzymatic digestion of these carbohydrates hereTransports brokendown carbohydrates in the body The monosaccharide units, glucose, galactose and fructose are transported through the wall of the small intestine and then into the portal vein which then takes these elements
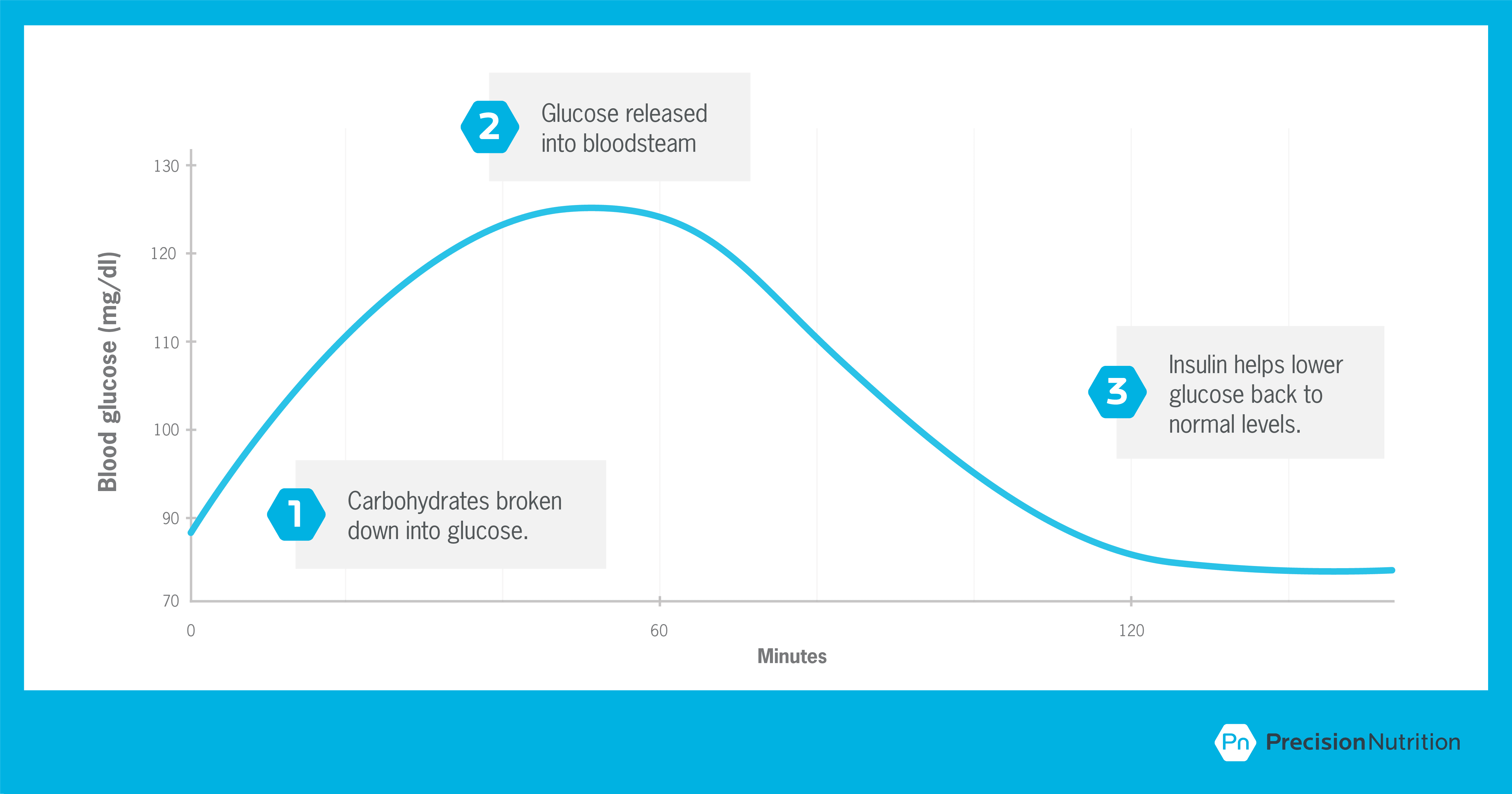



The Truth About Carbs Insulin And Weight Loss Precision Nutrition
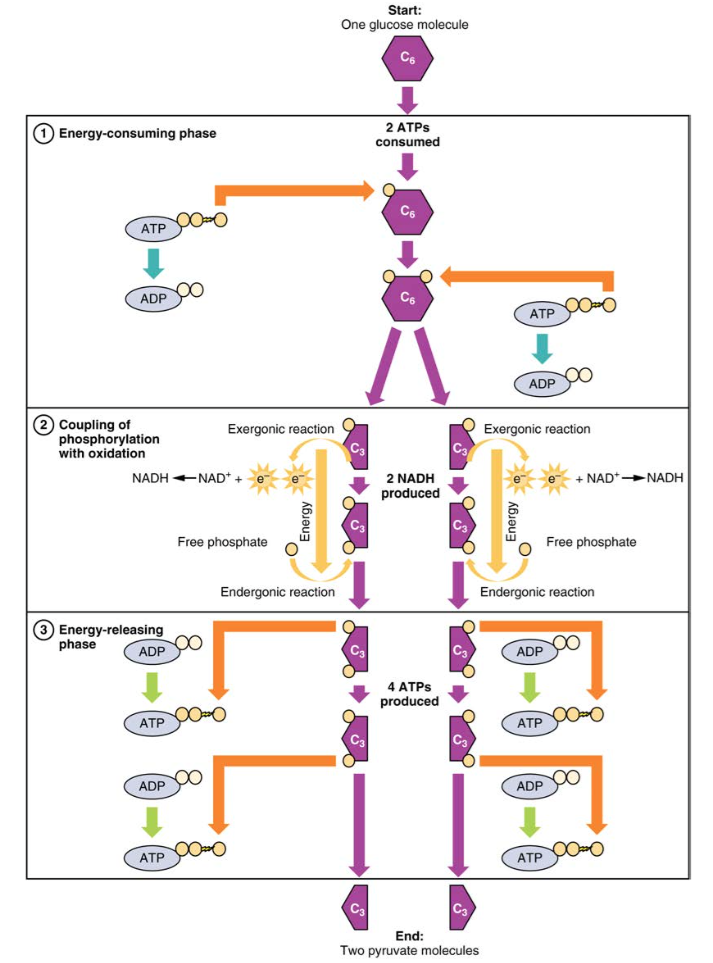



Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Ii
Sucrase breaks sucrose into glucose and fructose molecules Maltase breaks the bond between the two glucose units of maltose, and lactase breaks the bond between the galactose and glucose units of lactose Once carbohydrates are chemically broken down into single sugar units they are then transported into the inside of intestinal cellsPlants form starches, which are also called complex carbohydrates, by stringing together sugars When you eat starchy foods, the starches are broken down into sugars, including glucose, maltotriose and maltose, by an enzyme calledIn the small intestine, carbohydrates get further broken down into single carbohydrate units called monosaccharide These single molecules get absorbed across the intestine wall and are sent through the blood stream Carbohydrate in the blood is in



1



Digestion Storyboard By Oliversmith
Starch breaks down to shorter glucose chains This process starts in the mouth with salivary amylaseFiber Both simple and complex carbohydrates break down into glucose (aka blood sugar) A simple carb is one that's comprised of one or two sugar molecules, while a complex carb contains three orAll the carbohydrates you eat and drink are broken down into glucose The type, and amount, you consume can make a difference to your blood glucose levels and diabetes management There are different ways to describe carbohydrates One way of doing this is to group them into those that contain mostly starch (such as bread, rice, pasta, potatoes
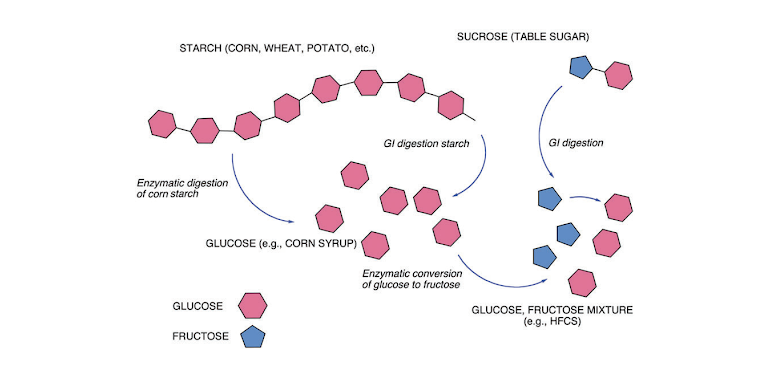



Crossfit An Introduction To Metabolism




3yjkv1u6pkvxwm
Starch is the stored form of sugars in plants and is made up of amylose and amylopectin (both polymers of glucose) Plants are able to synthesize glucose, and the excess glucose is stored as starch in different plant parts, including roots and seeds The starch that is consumed by animals is broken down into smaller molecules, such as glucoseCarbohydrates are your body's main energy source During digestion, sugar (simple carbohydrates) and starches (complex carbohydrates) break down into blood sugar (glucose) If you consume too much carbohydraterich food at one time, your blood sugar levels may rise too high, which can be problematicThe other disaccharides are broken down and converted into their two monosaccharide units How the body absorbs &



1
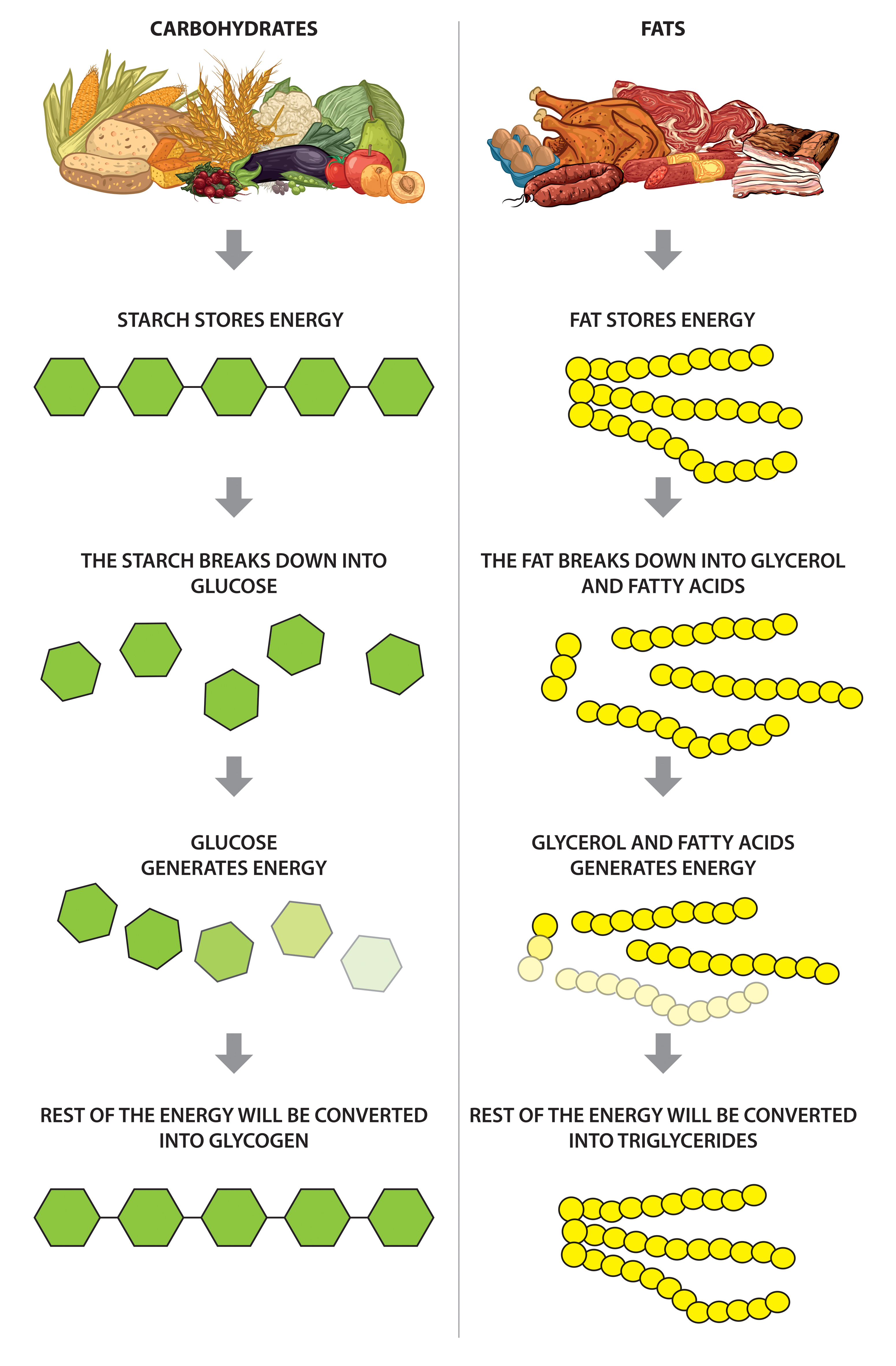



Carbohydrates Timing
When people eat a food containing carbohydrates, the digestive system breaks down the digestible ones into sugar, which enters the blood As blood sugar levels rise, the pancreas produces insulin, a hormone that prompts cells to absorb blood sugar for energy or storage As cells absorb blood sugar, levels in the bloodstream begin to fallCarbohydrates break down into glucose molecules When used as energy, carbohydrates fuel become fuel for your muscles and brain If your body does not have any use for the glucose, it is converted into glycogen and stored it in the liver and muscles as an energy reserve Your body can store about a half a day's supply of glycogenAfter a meal, the blood sugar (glucose) level rises as carbohydrate is digested This signals the beta cells of the pancreas to release insulin into the bloodstream Insulin helps glucose enter the body's cells to be used for energy If all the glucose is not needed for energy, some of it is stored in fat cells and in the liver as glycogen




Carbohydrates Singapore Heart Foundation
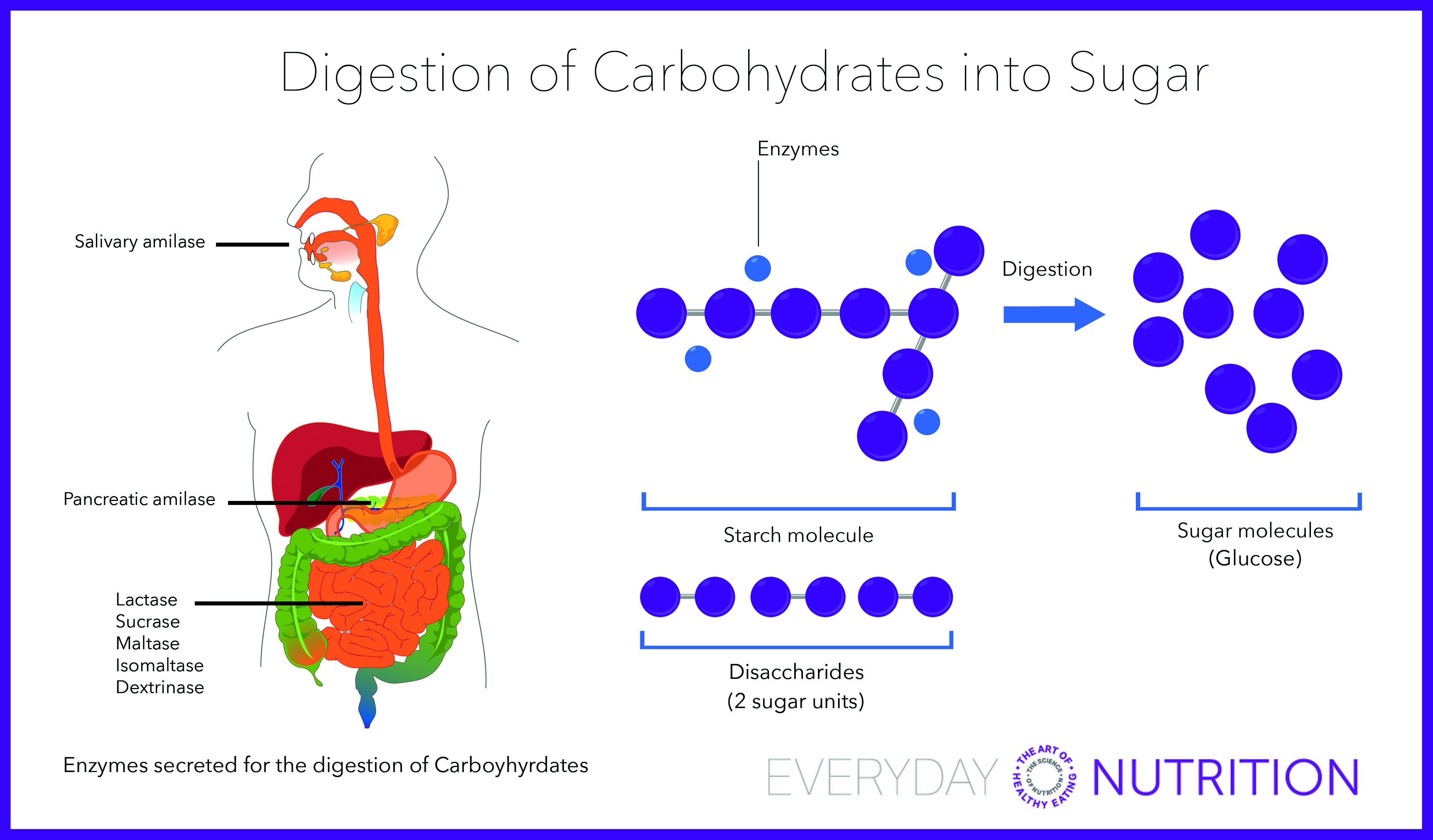



Everyday Nutrition The First Thing You Should Do For Your Health Better Energy And Weightloss
As carbohydrates are eaten, the digestive tract breaks them down into monosaccharide units, or glucose The glucose enters the bloodstream and travels first to the brain, which runs entirely on energy from glucose After the glucose needs of the brain have been met, the remaining glucose travels to the other tissues of the bodySucrase breaks sucrose into glucose and fructose molecules Maltase breaks the bond between the two glucose units of maltose, and lactase breaks the bond between galactose and glucose Once carbohydrates are chemically broken down into single sugar units they are then transported into the inside of intestinal cellsWhen carbohydrates are broken down into glucose within the blood, the body will Use insulin to help fuel the body's cells Use insulin to turn any remaining excess of glucose in the blood into fat for storage Carbohydrates provide energy and therefore if you have too high a level of carbohydrate in your diet this can lead to weight gain




How To Eat Carbs And Stay Healthy How To Stay Healthy Food Facts Carbohydrates



Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates
1 When you eat food that contains carbohydrates, you break down the carbohydrates into a monosaccharide called _____ glucose_____ If you don't use this monosaccharide, you body can store it in the liver in the form of _____glycogen_____ 2




Macronutrients A Simple Guide To Macros Avita Health System
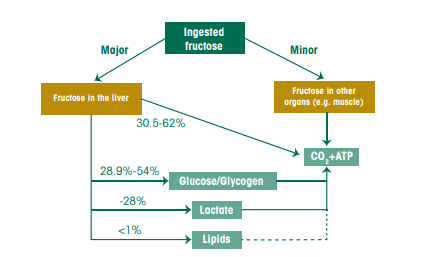



Carbohydrate Digestion And Absorption The Canadian Sugar Institute



Where In The Body Are Carbohydrates Broken Down Quora




Carbohydrate Digestion Nutritional Doublethink
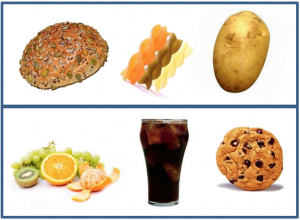



Healthy Eating And Lifestyle Walsall Healthcare Nhs Trust




Carbohydrates Ppt Download
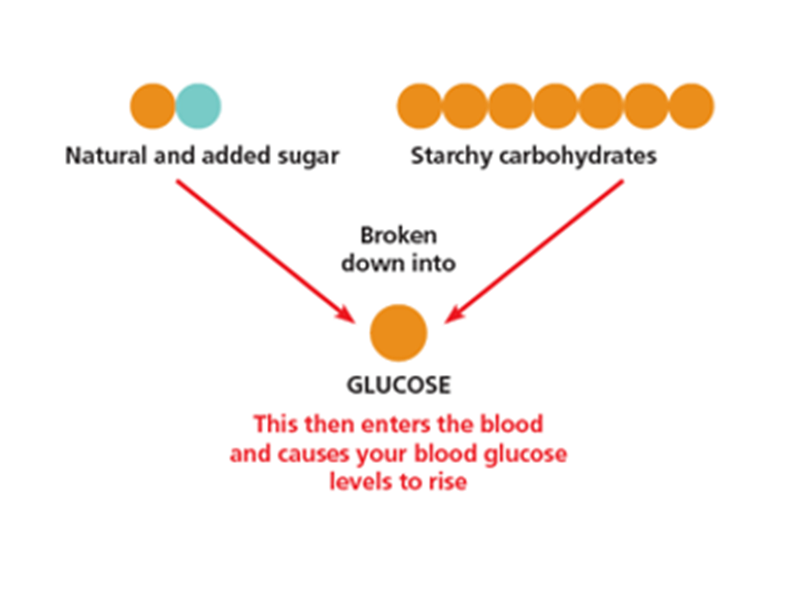



Understanding Carbohydrates Know Diabetes
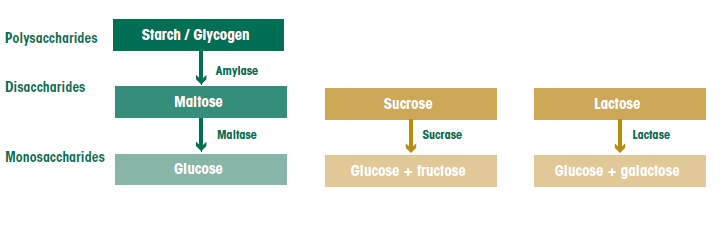



Carbohydrate Digestion And Absorption The Canadian Sugar Institute
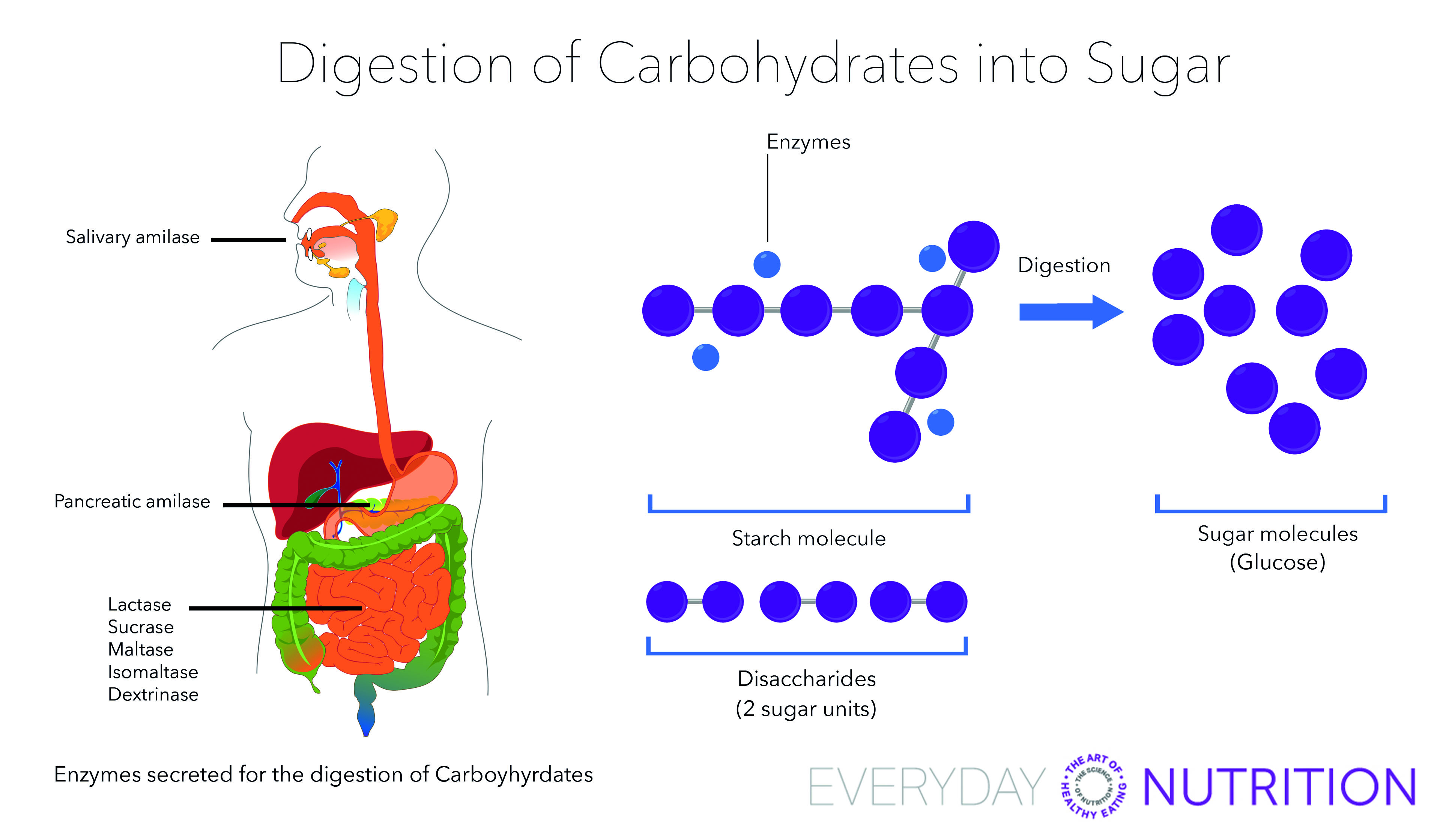



Everyday Nutrition Digestion Of Carbohydrates Into Sugar




Carbohydrates In Pet Food Pfma




Be Carb Smart With Purition Purition Usa




What Are Macronutrients Healthy Outcome For Teens




Carbohydrate Metabolism Wikipedia



Carbohydrate No Fructose



Why Is It That During Transportation Of Carbohydrates In Plants It Is In The Form Of Sucrose But In Animals It Is In The Form Of Glucose Socratic




Tracking Carbs Through The Body Diabetes And Carb Counting For Dummies For Dummies Lifestyle 1st Edition




What Are Carbohydrates Benefits Functions Best Sources Diets More Everyday Health




How Ketosis Ketones Works Learn The Full Process Of Ketosis




Hidden Sugars In Commercial Pet Foods By Canine Nutritionist Narelle Cooke Guides Big Dog Pet Foods



Carbohydrate Metabolism Welcome To Bio Stud



Digestive System Processes Biology For Majors Ii



Carbohydrates




Confused By Diabetes Here S A Simple Explanation Ethos Health




Carbohydrate Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary




Lesson 1 Page3




The Mysteries Of Digestion Unraveled Embracing Motherhood



Fueling Your Body Unit 5




Know Your Complex Simple And Refined Carbs



Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates Proteins And Fats



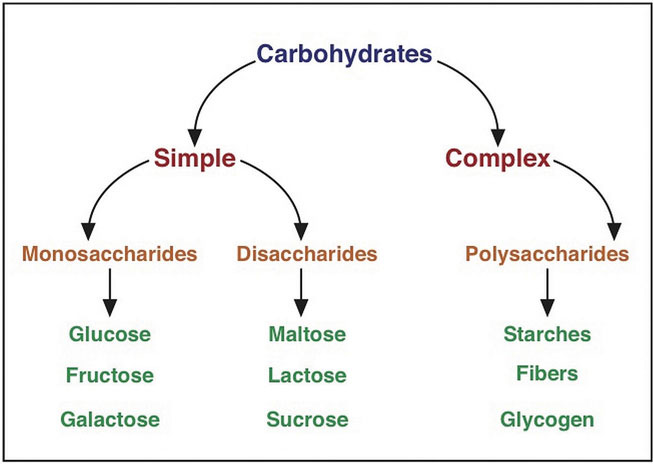
Types Of Carbohydrates




World Foods Feedback Carbs Cals



Carbohydrates




17 1 3 How Do The Macronutrients Provide Atp Medicine Libretexts
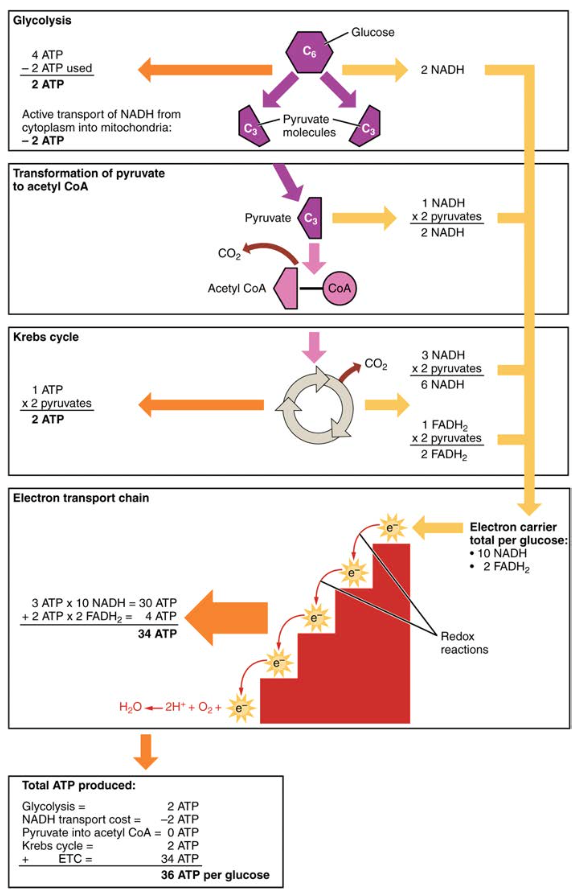



Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Ii




Carbohydrate Digestion Fermentation The Microbiome




4 2 Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates Medicine Libretexts




Digestive System Processes Biology For Majors Ii




Defining Carbohydrates Fats And Protein Fitivate




Carbohydrates Singapore Heart Foundation




Digestive System Processes Biology For Majors Ii




Carbohydrates Metabolism Assays Biovision Inc
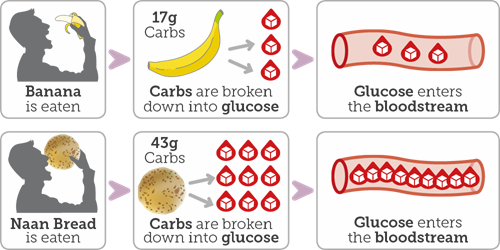



Carbohydrate Counting Know Diabetes



Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates



Carbohydrates How Food Works Howstuffworks




Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Ii




What Is Diabetes Diabetes Specialist Team Aims And




Carbohydrate Definition Classification Examples Britannica



Differences Between Sugar And Starch Difference Between



Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates Human Nutrition Deprecated



Www Naspghan Org Files Documents Pdfs Training Curriculum Resources Physiology Series Carbohydrate Digestion Naspghan Pdf
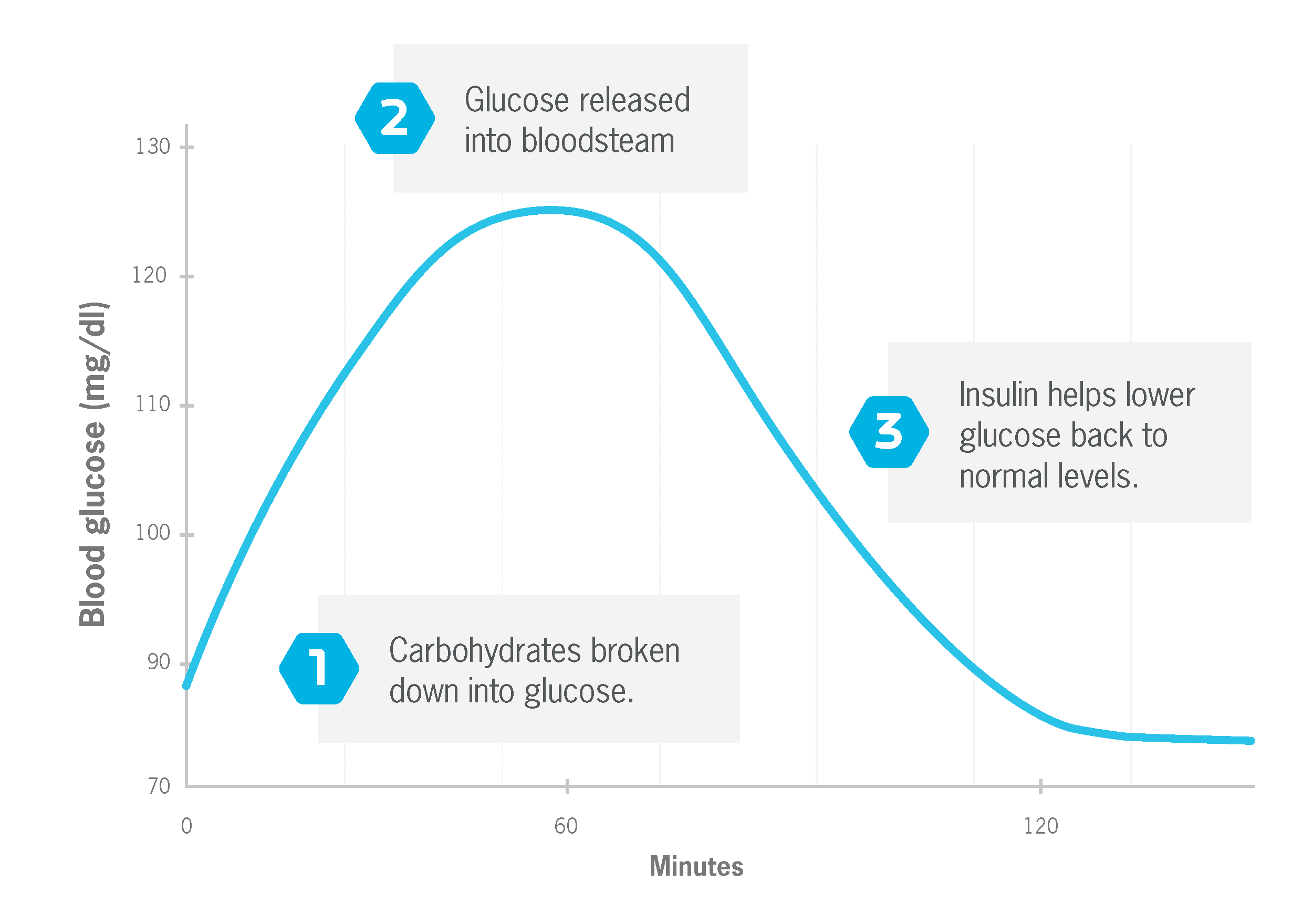



The Truth About Carbs Insulin And Weight Loss Precision Nutrition



Why Carbs Sugar And Insulin Cause Acne Goodglow Co




Living With Diabetes 3 3 Gut Openlearn Open University Sk1 2



1



Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Ii




Carbohydrates



Chemical Digestion Boundless Anatomy And Physiology



Www Naspghan Org Files Documents Pdfs Training Curriculum Resources Physiology Series Carbohydrate Digestion Naspghan Pdf



A Closer Look At Carbohydrates




3 3 Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates Medicine Libretexts



Types Of Carbohydrates Our Bodies Need Do You Know Your Carbs Well Love For Healthy Food




What Are Carbohydrates A Concise Guide
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/simple-and-complex-carbohydrates-and-diabetes-1087570-ADD-FINAL-V2-d27e373ab541449ba70bb26ff5f7cf71.png)



What To Know About Simple Vs Complex Carbohydrates



Starch Pmg Biology
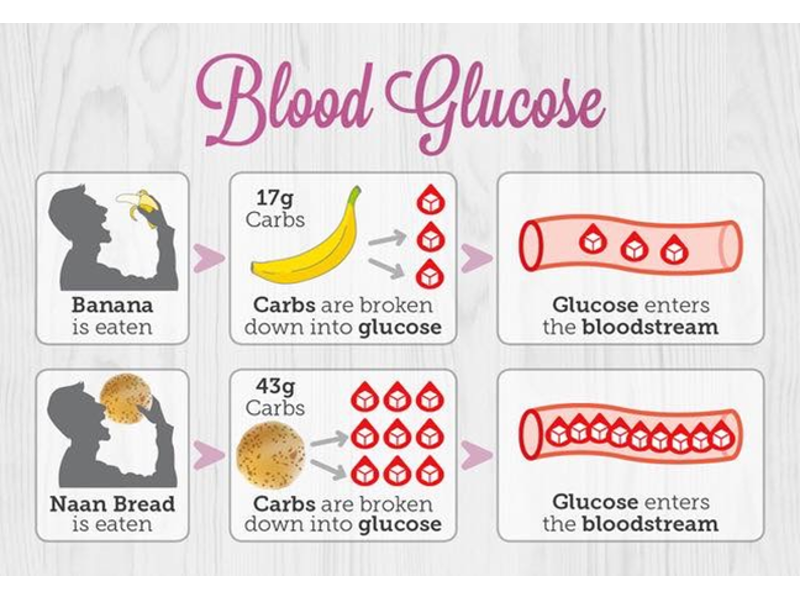



Understanding Carbohydrates Know Diabetes




Glycogenolysis Biochemistry Britannica




Carbohydrate Their Types And Sources Carbohydrates Youtube



Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates
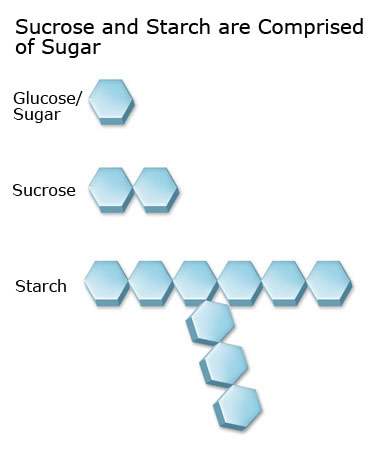



Understanding Carbohydrates Diabetes Education Online




24 3 Lipid Metabolism Anatomy Physiology
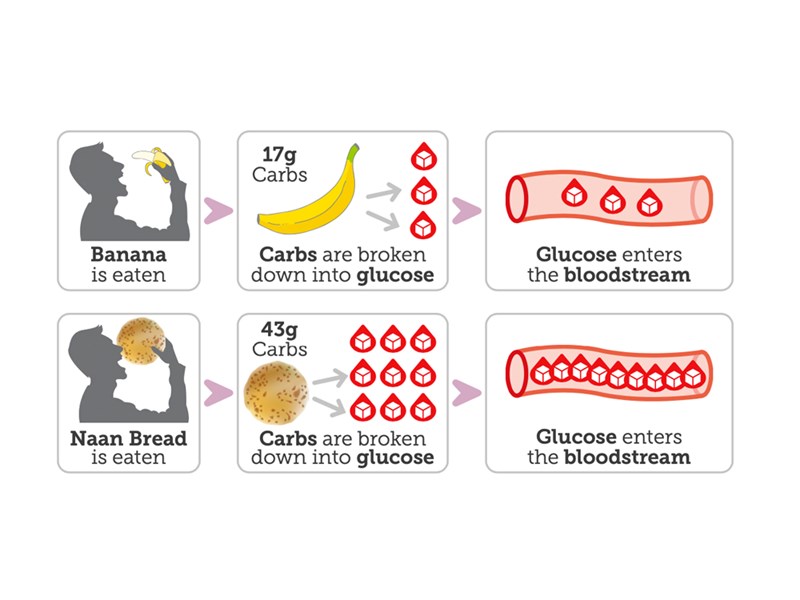



Cultural Diets Know Diabetes




9 Absorption Of Carbohydrates Amino Acids And Lipids Flashcards Quizlet



Types Of Carbohydrates



Carbohydrates
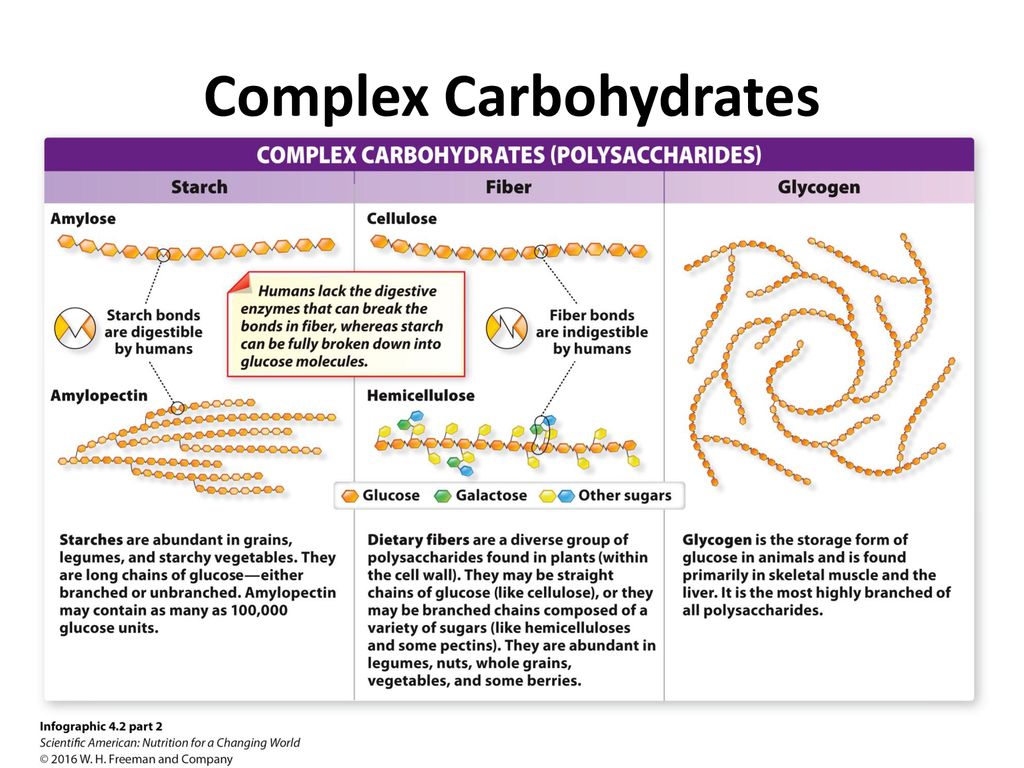



Carbohydrates Ppt Download




Macrofare What Is Ketosis Most People Think That Ketosis Occurs When You Eat Low Carb And High Fat Sure There S Truth To That But It S Not That Simple Our Bodies Naturally



Www Naspghan Org Files Documents Pdfs Training Curriculum Resources Physiology Series Carbohydrate Digestion Naspghan Pdf




Carbohydrate Definition Classification Examples Britannica




Digestive System Processes Biology For Majors Ii




What You Should Eat Before And After Exercise



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿